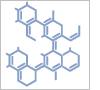
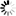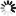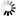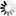Potassium+trifluoro(3-oxocyclopentyl)borate
Artikel-Nr:
(BOSSBS-3348R)
Lieferant:
Bioss
Hersteller-Artikelnummer::
BS-3348R
Lokale Artikelnummer::
BOSSBS-3348R
Beschreibung:
PSD 93 is believed to participate in the clustering of certain proteins, including N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptors and shaker-type potassium channels at the synaptic membrane. There are two principal modes of interaction between PSD 93 and other proteins. NMDA receptors and shaker-type potassium channels both share C-terminal sequence homology consisting of a threonine/serine-X-valine-COOH (T/SXV) motif. Other neuronal proteins that share this motif (beta 1 adrenergic receptor, some serotonin receptors, some sodium channel subunits, and additional potassium channel subunits) may interact with PSD 93 by binding to its PDZ domains. Neuronal nitric oxide synthase (nNOS), which lacks the T/SXV motif but which has its own PDZ domain, has been shown to associate with PSD 93 in vitro through a pseudo-homotypic PDZ-PDZ interaction.
VE:
1 * 100 µl
Artikel-Nr:
(BOSSBS-2436R-A350)
Lieferant:
Bioss
Hersteller-Artikelnummer::
BS-2436R-A350
Lokale Artikelnummer::
BOSSBS-2436R-A350
Beschreibung:
Potassium channels are present in most mammalian cells, where they participate in a wide range of physiologic responses. The protein encoded by this gene is an integral membrane protein and inward-rectifier type potassium channel. The encoded protein, which has a greater tendency to allow potassium to flow into a cell rather than out of a cell, is controlled by G-proteins and is found associated with the sulfonylurea receptor SUR. Mutations in this gene are a cause of familial persistent hyperinsulinemic hypoglycemia of infancy (PHHI), an autosomal recessive disorder characterized by unregulated insulin secretion. Defects in this gene may also contribute to autosomal dominant non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus type II (NIDDM), transient neonatal diabetes mellitus type 3 (TNDM3), and permanent neonatal diabetes mellitus (PNDM). Multiple alternatively spliced transcript variants that encode different protein isoforms have been described for this gene. [provided by RefSeq]
VE:
1 * 100 µl
Lieferant:
CHEMPUR SILANE
Beschreibung:
N-Methyl-N-(trimethylsilyl)trifluoracetamid
Artikel-Nr:
(1545500.)
Lieferant:
USP
Hersteller-Artikelnummer::
1545500
Lokale Artikelnummer::
USPH1545500
Beschreibung:
USP Reference Standards are specified for use in conducting official USP–NF tests and assays. USP also provides Reference Standards specified in the Food Chemicals Codex as well as authentic substances—high-quality chemical samples—as a service to analytical, clinical, pharmaceutical and research laboratories. To confirm accuracy and reproducibility, USP Reference Standards are rigorously tested and evaluated by multiple independent laboratories including USP, commercial, regulatory, and academic labs. USP also provide publicly available, official documentary standards for pharmaceutical ingredients in the USP–NF that link directly with our primary reference standards.
VE:
1 * 200 mg
Lieferant:
FLUOROCHEM
Beschreibung:
2,3,4-Trifluorbenzoylchlorid
Artikel-Nr:
(BOSSBS-12181R-CY7)
Lieferant:
Bioss
Hersteller-Artikelnummer::
BS-12181R-CY7
Lokale Artikelnummer::
BOSSBS-12181R-CY7
Beschreibung:
Potassium channels are present in most mammalian cells, where they participate in a wide range of physiologic responses. The protein encoded by this gene is an integral membrane protein and inward-rectifier type potassium channel. The encoded protein, which has a greater tendency to allow potassium to flow into a cell rather than out of a cell, is controlled by G-proteins and is found associated with the sulfonylurea receptor SUR. Mutations in this gene are a cause of familial persistent hyperinsulinemic hypoglycemia of infancy (PHHI), an autosomal recessive disorder characterized by unregulated insulin secretion. Defects in this gene may also contribute to autosomal dominant non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus type II (NIDDM), transient neonatal diabetes mellitus type 3 (TNDM3), and permanent neonatal diabetes mellitus (PNDM). Multiple alternatively spliced transcript variants that encode different protein isoforms have been described for this gene. [provided by RefSeq]
VE:
1 * 100 µl
Artikel-Nr:
(BOSSBS-12181R-A750)
Lieferant:
Bioss
Hersteller-Artikelnummer::
BS-12181R-A750
Lokale Artikelnummer::
BOSSBS-12181R-A750
Beschreibung:
Potassium channels are present in most mammalian cells, where they participate in a wide range of physiologic responses. The protein encoded by this gene is an integral membrane protein and inward-rectifier type potassium channel. The encoded protein, which has a greater tendency to allow potassium to flow into a cell rather than out of a cell, is controlled by G-proteins and is found associated with the sulfonylurea receptor SUR. Mutations in this gene are a cause of familial persistent hyperinsulinemic hypoglycemia of infancy (PHHI), an autosomal recessive disorder characterised by unregulated insulin secretion. Defects in this gene may also contribute to autosomal dominant non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus type II (NIDDM), transient neonatal diabetes mellitus type 3 (TNDM3), and permanent neonatal diabetes mellitus (PNDM). Multiple alternatively spliced transcript variants that encode different protein isoforms have been described for this gene.
VE:
1 * 100 µl
Artikel-Nr:
(BOSSBS-12175R-A647)
Lieferant:
Bioss
Hersteller-Artikelnummer::
BS-12175R-A647
Lokale Artikelnummer::
BOSSBS-12175R-A647
Beschreibung:
Voltage-gated potassium (Kv) channels represent the most complex class of voltage-gated ion channels from both functional and structural standpoints. Their diverse functions include regulating neurotransmitter release, heart rate, insulin secretion, neuronal excitability, epithelial electrolyte transport, smooth muscle contraction, and cell volume. This gene encodes a member of the potassium channel, voltage-gated, subfamily G. This member is a gamma subunit functioning as a modulatory molecule. Alternative splicing results in two transcript variants encoding distinct isoforms. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008].
VE:
1 * 100 µl
Artikel-Nr:
(BOSSBS-12175R-A350)
Lieferant:
Bioss
Hersteller-Artikelnummer::
BS-12175R-A350
Lokale Artikelnummer::
BOSSBS-12175R-A350
Beschreibung:
Voltage-gated potassium (Kv) channels represent the most complex class of voltage-gated ion channels from both functional and structural standpoints. Their diverse functions include regulating neurotransmitter release, heart rate, insulin secretion, neuronal excitability, epithelial electrolyte transport, smooth muscle contraction, and cell volume. This gene encodes a member of the potassium channel, voltage-gated, subfamily G. This member is a gamma subunit functioning as a modulatory molecule. Alternative splicing results in two transcript variants encoding distinct isoforms. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008].
VE:
1 * 100 µl
Artikel-Nr:
(BOSSBS-12174R-A647)
Lieferant:
Bioss
Hersteller-Artikelnummer::
BS-12174R-A647
Lokale Artikelnummer::
BOSSBS-12174R-A647
Beschreibung:
Voltage-gated potassium (Kv) channels represent the most complex class of voltage-gated ion channels from both functional and structural standpoints. Their diverse functions include regulating neurotransmitter release, heart rate, insulin secretion, neuronal excitability, epithelial electrolyte transport, smooth muscle contraction, and cell volume. This gene encodes a member of the potassium channel, voltage-gated, subfamily G. This gene is abundantly expressed in skeletal muscle. Multiple alternatively spliced transcript variants have been found in normal and cancerous tissues. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008].
VE:
1 * 100 µl
Artikel-Nr:
(BOSSBS-12175R-A750)
Lieferant:
Bioss
Hersteller-Artikelnummer::
BS-12175R-A750
Lokale Artikelnummer::
BOSSBS-12175R-A750
Beschreibung:
Voltage-gated potassium (Kv) channels represent the most complex class of voltage-gated ion channels from both functional and structural standpoints. Their diverse functions include regulating neurotransmitter release, heart rate, insulin secretion, neuronal excitability, epithelial electrolyte transport, smooth muscle contraction, and cell volume. This gene encodes a member of the potassium channel, voltage-gated, subfamily G. This member is a gamma subunit functioning as a modulatory molecule. Alternative splicing results in two transcript variants encoding distinct isoforms.
VE:
1 * 100 µl
Artikel-Nr:
(BOSSBS-12175R-A680)
Lieferant:
Bioss
Hersteller-Artikelnummer::
BS-12175R-A680
Lokale Artikelnummer::
BOSSBS-12175R-A680
Beschreibung:
Voltage-gated potassium (Kv) channels represent the most complex class of voltage-gated ion channels from both functional and structural standpoints. Their diverse functions include regulating neurotransmitter release, heart rate, insulin secretion, neuronal excitability, epithelial electrolyte transport, smooth muscle contraction, and cell volume. This gene encodes a member of the potassium channel, voltage-gated, subfamily G. This member is a gamma subunit functioning as a modulatory molecule. Alternative splicing results in two transcript variants encoding distinct isoforms.
VE:
1 * 100 µl
Artikel-Nr:
(900010ZK)
Lieferant:
VWR Chemicals
Lokale Artikelnummer::
VWRC900010ZK
Beschreibung:
Die Isolierung von Mikroorganismen erfordert häufig die Nutzung selektiver Medien. Die hier dargestellten Supplemente sind in Vials und Flaschen erhältlich. Das zur Verwendung mit dem vorgesehenen Nährmedium ist in der unten stehenden Tabelle angegeben. Sofern nicht anders angegeben, wird jedes Vial in der Regel für die Supplementierung von 500 ml Medien verwendet (umfassende Informationen in den auf Anfrage erhältlichen Datenblättern).
VE:
1 * 100 mL
Lieferant:
Sigma-Aldrich
Beschreibung:
1,1,1-Trifluoriodethan, Sigma-Aldrich®
Artikel-Nr:
(BOSSBS-6674R-A350)
Lieferant:
Bioss
Hersteller-Artikelnummer::
BS-6674R-A350
Lokale Artikelnummer::
BOSSBS-6674R-A350
Beschreibung:
KCNK3 encodes one of the members of the superfamily of potassium channel proteins containing two pore forming P domains. The gene product is an outwardly rectifying channel that is sensitive to changes in extracellular pH and is inhibited by extracellular acidification. Also referred to as an acid sensitive potassium channel, it is activated by the anesthetics halothane and isoflurane. Although three transcripts are detected in northern blots, there is currently no sequence available to confirm transcript variants for this gene.
VE:
1 * 100 µl
Artikel-Nr:
(BOSSBS-6674R-A555)
Lieferant:
Bioss
Hersteller-Artikelnummer::
BS-6674R-A555
Lokale Artikelnummer::
BOSSBS-6674R-A555
Beschreibung:
KCNK3 encodes one of the members of the superfamily of potassium channel proteins containing two pore forming P domains. The gene product is an outwardly rectifying channel that is sensitive to changes in extracellular pH and is inhibited by extracellular acidification. Also referred to as an acid sensitive potassium channel, it is activated by the anesthetics halothane and isoflurane. Although three transcripts are detected in northern blots, there is currently no sequence available to confirm transcript variants for this gene.
VE:
1 * 100 µl
Preis auf Anfrage
Lager für diesen Artikel ist begrenzt, kann aber in einem Lagerhaus in Ihrer Nähe zur Verfügung. Bitte stellen Sie sicher, dass Sie in sind angemeldet auf dieser Seite, so dass verfügbare Bestand angezeigt werden können. Wenn das
Lager für diesen Artikel ist begrenzt, kann aber in einem Lagerhaus in Ihrer Nähe zur Verfügung. Bitte stellen Sie sicher, dass Sie in sind angemeldet auf dieser Seite, so dass verfügbare Bestand angezeigt werden können. Wenn das
Dieses Produkt kann nur an eine Lieferadresse versandt werden die über die entsprechende Lizenzen verfügt. Für weitere Hilfe bitte kontaktieren Sie Ihr VWR Vertriebszentrum.
-Additional Documentation May be needed to purchase this item. A VWR representative will contact you if needed.
Dieses Produkt wurde von Ihrer Organisation gesperrt. Bitte kontaktieren Sie Ihren Einkauf für weitere Informationen.
Dieses Produkt ist Ersatz für den von Ihnen gewünschten Artikel.
Dieses Produkt ist nicht mehr verfügbar. Bitte kontaktieren Sie den VWR Kundenservice.
|
|||||||||