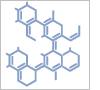
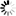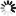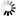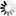1-(2-Cyanophenyl)-4-piperidinecarboxylic+acid
Artikel-Nr:
(BOSSBS-11891R-A647)
Lieferant:
Bioss
Hersteller-Artikelnummer::
BS-11891R-A647
Lokale Artikelnummer::
BOSSBS-11891R-A647
Beschreibung:
Myotrophin (V-1 protein) is a ubiquitously expressed cytoplasmic protein that can translocate to the nucleus during sustained NFkB activation. The gene encoding for this protein localizes to chromosome 7q33. Myotrophin may be involved in cerebellar morphogenesis and contains an acetylated N-terminus and 2.5 internal 33 amino acid ankyrin repeats. It is important in the differentiation of cerebellar neurons, particularly of granule cells. The 117 amino acid protein has been associated with, and able to induce, cardiac hypertrophy. Myotrophin increases protooncogene, ANF and Beta-Myosin heavy chain transcript levels. Myotrophin is upregulated when myocytes undergo cyclic stretch or are treated with tumor necrosis factor Alpha (TNF Alpha) or interleukin-1Beta. Highest levels of Myotrophin are detected in brain and lowest levels in skeletal muscle.
VE:
1 * 100 µl
Artikel-Nr:
(BOSSBS-11891R-HRP)
Lieferant:
Bioss
Hersteller-Artikelnummer::
BS-11891R-HRP
Lokale Artikelnummer::
BOSSBS-11891R-HRP
Beschreibung:
Myotrophin (V-1 protein) is a ubiquitously expressed cytoplasmic protein that can translocate to the nucleus during sustained NFkB activation. The gene encoding for this protein localizes to chromosome 7q33. Myotrophin may be involved in cerebellar morphogenesis and contains an acetylated N-terminus and 2.5 internal 33 amino acid ankyrin repeats. It is important in the differentiation of cerebellar neurons, particularly of granule cells. The 117 amino acid protein has been associated with, and able to induce, cardiac hypertrophy. Myotrophin increases protooncogene, ANF and Beta-Myosin heavy chain transcript levels. Myotrophin is upregulated when myocytes undergo cyclic stretch or are treated with tumor necrosis factor Alpha (TNF Alpha) or interleukin-1Beta. Highest levels of Myotrophin are detected in brain and lowest levels in skeletal muscle.
VE:
1 * 100 µl
Artikel-Nr:
(BOSSBS-13271R-CY5)
Lieferant:
Bioss
Hersteller-Artikelnummer::
BS-13271R-CY5
Lokale Artikelnummer::
BOSSBS-13271R-CY5
Beschreibung:
The UDP-N-acetyl-alpha-D-galactosamine:polypeptide N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase (GalNAc-T) family of enzymes are substrate-specific proteins that catalyze the transfer of GalNAc (N-acetylgalactosamine) to serine and threonine residues onto various proteins, thereby initiating mucin-type O-linked glycosylation in the Golgi apparatus. GalNAc-T11 (Polypeptide N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase 11), also known as UDP-GalNAc:polypeptide N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase 11, is a 608 amino acid protein that catalyzes glycosylation of Muc1, Muc4.1 and EA2, though it does not display enzymatic preference for erythropoitein. The N-terminal domain is involved in substrate binding and manganese coordination, while the C-terminal domain is involved in UDP-Gal binding and catalytic reaction. GalNAc-T11 is highly expressed in kidney tubules, though it is not expressed in glomeruli. There are two isoforms of GalNAc-T11 that are produced as a result of alternative splicing events.
VE:
1 * 100 µl
Artikel-Nr:
(BOSSBS-3026R-A750)
Lieferant:
Bioss
Hersteller-Artikelnummer::
BS-3026R-A750
Lokale Artikelnummer::
BOSSBS-3026R-A750
Beschreibung:
The protein encoded by this gene is a regulatory subunit of the AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK). AMPK is a heterotrimer consisting of an alpha catalytic subunit, and non-catalytic beta and gamma subunits. AMPK is an important energy-sensing enzyme that monitors cellular energy status. In response to cellular metabolic stresses, AMPK is activated, and thus phosphorylates and inactivates acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACC) and beta-hydroxy beta-methylglutaryl-CoA reductase (HMGCR), key enzymes involved in regulating de novo biosynthesis of fatty acid and cholesterol. This subunit may be a positive regulator of AMPK activity. The myristoylation and phosphorylation of this subunit have been shown to affect the enzyme activity and cellular localization of AMPK. This subunit may also serve as an adaptor molecule mediating the association of the AMPK complex.
VE:
1 * 100 µl
Artikel-Nr:
(BOSSBS-8687R-CY5.5)
Lieferant:
Bioss
Hersteller-Artikelnummer::
BS-8687R-CY5.5
Lokale Artikelnummer::
BOSSBS-8687R-CY5.5
Beschreibung:
p53, a DNA-binding, oligomerization domain- and transcription activation domain-containing tumor suppressor, upregulates growth arrest and apoptosis-related genes in response to stress signals, thereby influencing programmed cell death, cell differentiation, and cell cycle control mechanisms. p53 localizes to the nucleus, yet can be chaperoned to the cytoplasm by the negative regulator, MDM2. MDM2 is an E3 ubiquitin ligase that is upregulated in the presence of active p53, where it poly-ubiquitinates p53 for proteasome targeting. p53 fluctuates between latent and active DNA-binding conformations and is differentially activated through posttranslational modifications, including phosphorylation and acetylation. Mutations in the DNA-binding domain (DBD) of p53, amino acids 110-286, can compromise energetically-favorable association with cis elements and are implicated in several human cancers.
VE:
1 * 100 µl
Artikel-Nr:
(BOSSBS-13271R-FITC)
Lieferant:
Bioss
Hersteller-Artikelnummer::
BS-13271R-FITC
Lokale Artikelnummer::
BOSSBS-13271R-FITC
Beschreibung:
The UDP-N-acetyl-alpha-D-galactosamine:polypeptide N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase (GalNAc-T) family of enzymes are substrate-specific proteins that catalyze the transfer of GalNAc (N-acetylgalactosamine) to serine and threonine residues onto various proteins, thereby initiating mucin-type O-linked glycosylation in the Golgi apparatus. GalNAc-T11 (Polypeptide N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase 11), also known as UDP-GalNAc:polypeptide N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase 11, is a 608 amino acid protein that catalyzes glycosylation of Muc1, Muc4.1 and EA2, though it does not display enzymatic preference for erythropoitein. The N-terminal domain is involved in substrate binding and manganese coordination, while the C-terminal domain is involved in UDP-Gal binding and catalytic reaction. GalNAc-T11 is highly expressed in kidney tubules, though it is not expressed in glomeruli. There are two isoforms of GalNAc-T11 that are produced as a result of alternative splicing events.
VE:
1 * 100 µl
Artikel-Nr:
(BOSSBS-3026R-CY7)
Lieferant:
Bioss
Hersteller-Artikelnummer::
BS-3026R-CY7
Lokale Artikelnummer::
BOSSBS-3026R-CY7
Beschreibung:
The protein encoded by this gene is a regulatory subunit of the AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK). AMPK is a heterotrimer consisting of an alpha catalytic subunit, and non-catalytic beta and gamma subunits. AMPK is an important energy-sensing enzyme that monitors cellular energy status. In response to cellular metabolic stresses, AMPK is activated, and thus phosphorylates and inactivates acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACC) and beta-hydroxy beta-methylglutaryl-CoA reductase (HMGCR), key enzymes involved in regulating de novo biosynthesis of fatty acid and cholesterol. This subunit may be a positive regulator of AMPK activity. The myristoylation and phosphorylation of this subunit have been shown to affect the enzyme activity and cellular localization of AMPK. This subunit may also serve as an adaptor molecule mediating the association of the AMPK complex. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008].
VE:
1 * 100 µl
Artikel-Nr:
(BOSSBS-13270R-A647)
Lieferant:
Bioss
Hersteller-Artikelnummer::
BS-13270R-A647
Lokale Artikelnummer::
BOSSBS-13270R-A647
Beschreibung:
The UDP-N-acetyl-alpha-D-galactosamine:polypeptide N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase (GalNAc-T) family of enzymes are substrate-specific proteins that catalyze the transfer of GalNAc (N-acetylgalactosaminyl) to serine and threonine residues of various proteins, thereby initiating mucin-type O-linked glycosylation in the Golgi apparatus. GalNAc-T10 (Polypeptide N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase 10), also known as UDP-GalNAc:polypeptide N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase 10, is a 603 amino acid single-pass type II membrane protein that prefers Muc5Ac and EA2 peptide substrates. The N-terminal domain is involved in substrate binding and manganese coordination, while the C-terminal domain is involved in UDP-Gal binding and catalytic reaction. GalNAc-T10 is widely expressed, with highest levels found in small intestine. There are four isoforms of GalNAc-T10 that are produced as a result of alternative splicing events.
VE:
1 * 100 µl
Artikel-Nr:
(BOSSBS-13274R-CY7)
Lieferant:
Bioss
Hersteller-Artikelnummer::
BS-13274R-CY7
Lokale Artikelnummer::
BOSSBS-13274R-CY7
Beschreibung:
The UDP-N-acetyl-alpha-D-galactosamine:polypeptide N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase (GalNAc-T) family of enzymes are substrate-specific proteins that catalyze the transfer of GalNAc (N-acetylgalactosamine) to serine and threonine residues onto various proteins, thereby initiating mucin-type O-linked glycosylation in the Golgi apparatus. GalNAc-T13 (Polypeptide N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase 13), also known as UDP-GalNAc:polypeptide N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase 13, is a 556 amino acid protein that displays much stronger enzymatic activity than GalNAc-1 towards GalNAc transfer to mucin peptides such as Muc5a and Muc7. The N-terminal domain is involved in substrate binding and manganese coordination, while the C-terminal domain is involved in UDP-Gal binding and catalytic reaction. With specific expression in the central nervous system, GalNAc-T13 may be responsible for the synthesis of Tn antigen in neuronal cells, which is a universal carcinoma marker on malignant cells.
VE:
1 * 100 µl
Artikel-Nr:
(BOSSBS-13274R-CY3)
Lieferant:
Bioss
Hersteller-Artikelnummer::
BS-13274R-CY3
Lokale Artikelnummer::
BOSSBS-13274R-CY3
Beschreibung:
The UDP-N-acetyl-alpha-D-galactosamine:polypeptide N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase (GalNAc-T) family of enzymes are substrate-specific proteins that catalyze the transfer of GalNAc (N-acetylgalactosamine) to serine and threonine residues onto various proteins, thereby initiating mucin-type O-linked glycosylation in the Golgi apparatus. GalNAc-T13 (Polypeptide N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase 13), also known as UDP-GalNAc:polypeptide N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase 13, is a 556 amino acid protein that displays much stronger enzymatic activity than GalNAc-1 towards GalNAc transfer to mucin peptides such as Muc5a and Muc7. The N-terminal domain is involved in substrate binding and manganese coordination, while the C-terminal domain is involved in UDP-Gal binding and catalytic reaction. With specific expression in the central nervous system, GalNAc-T13 may be responsible for the synthesis of Tn antigen in neuronal cells, which is a universal carcinoma marker on malignant cells.
VE:
1 * 100 µl
Lieferant:
BACHEM BIOCHEMICA
Beschreibung:
Acetyl-Pepstatin
Lieferant:
Sigma-Aldrich
Beschreibung:
1-(3-Methyl-2-pyrazinyl)ethanon, Sigma-Aldrich®
Lieferant:
FLUOROCHEM
Beschreibung:
1-(3-Ethyl-2-pyrazinyl)ethanon
Lieferant:
FLUOROCHEM
Beschreibung:
1-(3-Methyl-2-pyrazinyl)ethanon
Artikel-Nr:
(BOSSBS-4034R-CY7)
Lieferant:
Bioss
Hersteller-Artikelnummer::
BS-4034R-CY7
Lokale Artikelnummer::
BOSSBS-4034R-CY7
Beschreibung:
The pyruvate dehydrogenase (PDH) complex is a nuclear-encoded mitochondrial multienzyme complex that catalyzes the overall conversion of pyruvate to acetyl-CoA and CO(2), and provides the primary link between glycolysis and the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle. The PDH complex is composed of multiple copies of three enzymatic components: pyruvate dehydrogenase (E1), dihydrolipoamide acetyltransferase (E2) and lipoamide dehydrogenase(E3). The E1 enzyme is a heterotetramer of two alpha and two beta subunits. This gene encodes the E1 alpha 1 subunit containing the E1 active site, and plays a key role in the function of the PDH complex. Mutations in this gene are associated with pyruvate dehydrogenase E1-alpha deficiency and X-linked Leigh syndrome. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene.
VE:
1 * 100 µl
Artikel-Nr:
(BOSSBS-11891R-A488)
Lieferant:
Bioss
Hersteller-Artikelnummer::
BS-11891R-A488
Lokale Artikelnummer::
BOSSBS-11891R-A488
Beschreibung:
Myotrophin (V-1 protein) is a ubiquitously expressed cytoplasmic protein that can translocate to the nucleus during sustained NFkB activation. The gene encoding for this protein localizes to chromosome 7q33. Myotrophin may be involved in cerebellar morphogenesis and contains an acetylated N-terminus and 2.5 internal 33 amino acid ankyrin repeats. It is important in the differentiation of cerebellar neurons, particularly of granule cells. The 117 amino acid protein has been associated with, and able to induce, cardiac hypertrophy. Myotrophin increases protooncogene, ANF and Beta-Myosin heavy chain transcript levels. Myotrophin is upregulated when myocytes undergo cyclic stretch or are treated with tumor necrosis factor Alpha (TNF Alpha) or interleukin-1Beta. Highest levels of Myotrophin are detected in brain and lowest levels in skeletal muscle.
VE:
1 * 100 µl
Preis auf Anfrage
Lager für diesen Artikel ist begrenzt, kann aber in einem Lagerhaus in Ihrer Nähe zur Verfügung. Bitte stellen Sie sicher, dass Sie in sind angemeldet auf dieser Seite, so dass verfügbare Bestand angezeigt werden können. Wenn das
Lager für diesen Artikel ist begrenzt, kann aber in einem Lagerhaus in Ihrer Nähe zur Verfügung. Bitte stellen Sie sicher, dass Sie in sind angemeldet auf dieser Seite, so dass verfügbare Bestand angezeigt werden können. Wenn das
Dieses Produkt kann nur an eine Lieferadresse versandt werden die über die entsprechende Lizenzen verfügt. Für weitere Hilfe bitte kontaktieren Sie Ihr VWR Vertriebszentrum.
-Additional Documentation May be needed to purchase this item. A VWR representative will contact you if needed.
Dieses Produkt wurde von Ihrer Organisation gesperrt. Bitte kontaktieren Sie Ihren Einkauf für weitere Informationen.
Dieses Produkt ist Ersatz für den von Ihnen gewünschten Artikel.
Dieses Produkt ist nicht mehr verfügbar. Bitte kontaktieren Sie den VWR Kundenservice.
|
|||||||||