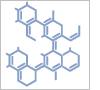
2-(4-Boc-piperazino)-2-(2-fluorphenyl)essigsäure
Artikel-Nr:
(BOSSBS-13521R-HRP)
Lieferant:
Bioss
Hersteller-Artikelnummer::
BS-13521R-HRP
Lokale Artikelnummer::
BOSSBS-13521R-HRP
Beschreibung:
G protein-coupled receptor 17, GPR17, also known as uracil nucleotide/cysteinyl leukotriene receptor or P2Y-like receptor (P2YL), is a 367 amino acid member of the G-protein coupled receptor 1 family of proteins. While GPR17 is expressed in kidney, heart and umbilical vein endothelial cells, it is expressed in the highest levels in the brain. Upon brain injury, the extracellular concentrations of nucleotides and cysteinyl leukotrienes (CysLTs), two families of endogenous signaling molecules, increase significantly at the site of damage. In some neurons, GPR17, a membrane receptor for uracil nucleotide and CysLTs, is upregulated as well, infiltrating the lesioned area. GPR17 is thought to play a role in mediating neuronal death, remodeling brain circuitries by microglia and initiating remyelination in damaged neurons. Two named isoforms of GPR17 exist as a result of alternative splicing events.
VE:
1 * 100 µl
Artikel-Nr:
(BOSSBS-6584R-A555)
Lieferant:
Bioss
Hersteller-Artikelnummer::
BS-6584R-A555
Lokale Artikelnummer::
BOSSBS-6584R-A555
Beschreibung:
This enzyme is involved in nucleotide metabolism: it produces dUMP, the immediate precursor of thymidine nucleotides and it decreases the intracellular concentration of dUTP so that uracil cannot be incorporated into DNA.
VE:
1 * 100 µl
Artikel-Nr:
(BOSSBS-1721R-A350)
Lieferant:
Bioss
Hersteller-Artikelnummer::
BS-1721R-A350
Lokale Artikelnummer::
BOSSBS-1721R-A350
Beschreibung:
This enzyme is involved in nucleotide metabolism: it produces dUMP, the immediate precursor of thymidine nucleotides and it decreases the intracellular concentration of dUTP so that uracil cannot be incorporated into DNA.
VE:
1 * 100 µl
Artikel-Nr:
(BOSSBS-1721R-A750)
Lieferant:
Bioss
Hersteller-Artikelnummer::
BS-1721R-A750
Lokale Artikelnummer::
BOSSBS-1721R-A750
Beschreibung:
This enzyme is involved in nucleotide metabolism: it produces dUMP, the immediate precursor of thymidine nucleotides and it decreases the intracellular concentration of dUTP so that uracil cannot be incorporated into DNA.
VE:
1 * 100 µl
Artikel-Nr:
(BOSSBS-6584R-A350)
Lieferant:
Bioss
Hersteller-Artikelnummer::
BS-6584R-A350
Lokale Artikelnummer::
BOSSBS-6584R-A350
Beschreibung:
This enzyme is involved in nucleotide metabolism: it produces dUMP, the immediate precursor of thymidine nucleotides and it decreases the intracellular concentration of dUTP so that uracil cannot be incorporated into DNA.
VE:
1 * 100 µl
Artikel-Nr:
(BOSSBS-6584R-FITC)
Lieferant:
Bioss
Hersteller-Artikelnummer::
BS-6584R-FITC
Lokale Artikelnummer::
BOSSBS-6584R-FITC
Beschreibung:
This enzyme is involved in nucleotide metabolism: it produces dUMP, the immediate precursor of thymidine nucleotides and it decreases the intracellular concentration of dUTP so that uracil cannot be incorporated into DNA.
VE:
1 * 100 µl
Artikel-Nr:
(BOSSBS-8288R)
Lieferant:
Bioss
Hersteller-Artikelnummer::
BS-8288R
Lokale Artikelnummer::
BOSSBS-8288R
Beschreibung:
Dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase (DPYD) catalyzes the first rate-limiting step of the NADPH-dependent catabolism of uracil and thymine to dihydrouracil and dihydrothymine; thus, a deficiency of DPYD leads to an accumulation of uracil and thymine. Abnormal concentrations of these metabolites in bodily fluids may be the cause of neurological disease and a contraindication for treatment of cancer patients with certain pyrimidine analogs. DPYD also catalyzes the anticancer agent 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) pathway and is involved in the efficacy and toxicity of 5-FU. Variations in DPYD concentration may arise from alterations at the transcriptional level of the dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase gene. Specifically, hypermethylation of the DPYD promoter downregulates dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase expression. Deficient DPYD alleles may constitute a risk factor for severe toxicity following treatment with 5-FU.Involvement in disease:Defects in DPYD are the cause of dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase deficiency (DPYD deficiency) ; also known as hereditary thymine-uraciluria or familial pyrimidinemia. DPYD deficiency is a disease characterized by persistent urinary excretion of excessive amounts of uracil, thymine and 5-hydroxymethyluracil. Patients suffering from this disease show a severe reaction to the anticancer drug 5-fluorouracil. This reaction includes stomatitis, Leukopenia, thrombocytopenia, hair loss, diarrhea, fever, marked weight loss, cerebellar ataxia, and neurologic symptoms, progressing to semicoma.
VE:
1 * 100 µl
Artikel-Nr:
(BOSSBS-6584R)
Lieferant:
Bioss
Hersteller-Artikelnummer::
BS-6584R
Lokale Artikelnummer::
BOSSBS-6584R
Beschreibung:
This enzyme is involved in nucleotide metabolism: it produces dUMP, the immediate precursor of thymidine nucleotides and it decreases the intracellular concentration of dUTP so that uracil cannot be incorporated into DNA.
VE:
1 * 100 µl
Artikel-Nr:
(BOSSBS-1721R-CY5)
Lieferant:
Bioss
Hersteller-Artikelnummer::
BS-1721R-CY5
Lokale Artikelnummer::
BOSSBS-1721R-CY5
Beschreibung:
This enzyme is involved in nucleotide metabolism: it produces dUMP, the immediate precursor of thymidine nucleotides and it decreases the intracellular concentration of dUTP so that uracil cannot be incorporated into DNA.
VE:
1 * 100 µl
Artikel-Nr:
(BOSSBS-6584R-CY7)
Lieferant:
Bioss
Hersteller-Artikelnummer::
BS-6584R-CY7
Lokale Artikelnummer::
BOSSBS-6584R-CY7
Beschreibung:
This enzyme is involved in nucleotide metabolism: it produces dUMP, the immediate precursor of thymidine nucleotides and it decreases the intracellular concentration of dUTP so that uracil cannot be incorporated into DNA.
VE:
1 * 100 µl
Artikel-Nr:
(BOSSBS-8288R-A350)
Lieferant:
Bioss
Hersteller-Artikelnummer::
BS-8288R-A350
Lokale Artikelnummer::
BOSSBS-8288R-A350
Beschreibung:
Dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase (DPYD) catalyzes the first rate-limiting step of the NADPH-dependent catabolism of uracil and thymine to dihydrouracil and dihydrothymine; thus, a deficiency of DPYD leads to an accumulation of uracil and thymine. Abnormal concentrations of these metabolites in bodily fluids may be the cause of neurological disease and a contraindication for treatment of cancer patients with certain pyrimidine analogs. DPYD also catalyzes the anticancer agent 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) pathway and is involved in the efficacy and toxicity of 5-FU. Variations in DPYD concentration may arise from alterations at the transcriptional level of the dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase gene. Specifically, hypermethylation of the DPYD promoter downregulates dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase expression. Deficient DPYD alleles may constitute a risk factor for severe toxicity following treatment with 5-FU.Involvement in disease:Defects in DPYD are the cause of dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase deficiency (DPYD deficiency) ; also known as hereditary thymine-uraciluria or familial pyrimidinemia. DPYD deficiency is a disease characterized by persistent urinary excretion of excessive amounts of uracil, thymine and 5-hydroxymethyluracil. Patients suffering from this disease show a severe reaction to the anticancer drug 5-fluorouracil. This reaction includes stomatitis, Leukopenia, thrombocytopenia, hair loss, diarrhea, fever, marked weight loss, cerebellar ataxia, and neurologic symptoms, progressing to semicoma.
VE:
1 * 100 µl
Artikel-Nr:
(BOSSBS-8288R-CY3)
Lieferant:
Bioss
Hersteller-Artikelnummer::
BS-8288R-CY3
Lokale Artikelnummer::
BOSSBS-8288R-CY3
Beschreibung:
Dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase (DPYD) catalyzes the first rate-limiting step of the NADPH-dependent catabolism of uracil and thymine to dihydrouracil and dihydrothymine; thus, a deficiency of DPYD leads to an accumulation of uracil and thymine. Abnormal concentrations of these metabolites in bodily fluids may be the cause of neurological disease and a contraindication for treatment of cancer patients with certain pyrimidine analogs. DPYD also catalyzes the anticancer agent 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) pathway and is involved in the efficacy and toxicity of 5-FU. Variations in DPYD concentration may arise from alterations at the transcriptional level of the dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase gene. Specifically, hypermethylation of the DPYD promoter downregulates dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase expression. Deficient DPYD alleles may constitute a risk factor for severe toxicity following treatment with 5-FU.Involvement in disease:Defects in DPYD are the cause of dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase deficiency (DPYD deficiency) ; also known as hereditary thymine-uraciluria or familial pyrimidinemia. DPYD deficiency is a disease characterized by persistent urinary excretion of excessive amounts of uracil, thymine and 5-hydroxymethyluracil. Patients suffering from this disease show a severe reaction to the anticancer drug 5-fluorouracil. This reaction includes stomatitis, Leukopenia, thrombocytopenia, hair loss, diarrhea, fever, marked weight loss, cerebellar ataxia, and neurologic symptoms, progressing to semicoma.
VE:
1 * 100 µl
Artikel-Nr:
(BOSSBS-8288R-CY5)
Lieferant:
Bioss
Hersteller-Artikelnummer::
BS-8288R-CY5
Lokale Artikelnummer::
BOSSBS-8288R-CY5
Beschreibung:
Dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase (DPYD) catalyzes the first rate-limiting step of the NADPH-dependent catabolism of uracil and thymine to dihydrouracil and dihydrothymine; thus, a deficiency of DPYD leads to an accumulation of uracil and thymine. Abnormal concentrations of these metabolites in bodily fluids may be the cause of neurological disease and a contraindication for treatment of cancer patients with certain pyrimidine analogs. DPYD also catalyzes the anticancer agent 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) pathway and is involved in the efficacy and toxicity of 5-FU. Variations in DPYD concentration may arise from alterations at the transcriptional level of the dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase gene. Specifically, hypermethylation of the DPYD promoter downregulates dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase expression. Deficient DPYD alleles may constitute a risk factor for severe toxicity following treatment with 5-FU.Involvement in disease:Defects in DPYD are the cause of dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase deficiency (DPYD deficiency) ; also known as hereditary thymine-uraciluria or familial pyrimidinemia. DPYD deficiency is a disease characterized by persistent urinary excretion of excessive amounts of uracil, thymine and 5-hydroxymethyluracil. Patients suffering from this disease show a severe reaction to the anticancer drug 5-fluorouracil. This reaction includes stomatitis, Leukopenia, thrombocytopenia, hair loss, diarrhea, fever, marked weight loss, cerebellar ataxia, and neurologic symptoms, progressing to semicoma.
VE:
1 * 100 µl
Artikel-Nr:
(BOSSBS-8288R-A647)
Lieferant:
Bioss
Hersteller-Artikelnummer::
BS-8288R-A647
Lokale Artikelnummer::
BOSSBS-8288R-A647
Beschreibung:
Dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase (DPYD) catalyzes the first rate-limiting step of the NADPH-dependent catabolism of uracil and thymine to dihydrouracil and dihydrothymine; thus, a deficiency of DPYD leads to an accumulation of uracil and thymine. Abnormal concentrations of these metabolites in bodily fluids may be the cause of neurological disease and a contraindication for treatment of cancer patients with certain pyrimidine analogs. DPYD also catalyzes the anticancer agent 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) pathway and is involved in the efficacy and toxicity of 5-FU. Variations in DPYD concentration may arise from alterations at the transcriptional level of the dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase gene. Specifically, hypermethylation of the DPYD promoter downregulates dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase expression. Deficient DPYD alleles may constitute a risk factor for severe toxicity following treatment with 5-FU.Involvement in disease:Defects in DPYD are the cause of dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase deficiency (DPYD deficiency) ; also known as hereditary thymine-uraciluria or familial pyrimidinemia. DPYD deficiency is a disease characterized by persistent urinary excretion of excessive amounts of uracil, thymine and 5-hydroxymethyluracil. Patients suffering from this disease show a severe reaction to the anticancer drug 5-fluorouracil. This reaction includes stomatitis, Leukopenia, thrombocytopenia, hair loss, diarrhea, fever, marked weight loss, cerebellar ataxia, and neurologic symptoms, progressing to semicoma.
VE:
1 * 100 µl
Artikel-Nr:
(BOSSBS-8288R-A750)
Lieferant:
Bioss
Hersteller-Artikelnummer::
BS-8288R-A750
Lokale Artikelnummer::
BOSSBS-8288R-A750
Beschreibung:
Dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase (DPYD) catalyzes the first rate-limiting step of the NADPH-dependent catabolism of uracil and thymine to dihydrouracil and dihydrothymine; thus, a deficiency of DPYD leads to an accumulation of uracil and thymine. Abnormal concentrations of these metabolites in bodily fluids may be the cause of neurological disease and a contraindication for treatment of cancer patients with certain pyrimidine analogs. DPYD also catalyzes the anticancer agent 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) pathway and is involved in the efficacy and toxicity of 5-FU. Variations in DPYD concentration may arise from alterations at the transcriptional level of the dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase gene. Specifically, hypermethylation of the DPYD promoter downregulates dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase expression. Deficient DPYD alleles may constitute a risk factor for severe toxicity following treatment with 5-FU.Involvement in disease:Defects in DPYD are the cause of dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase deficiency (DPYD deficiency) ; also known as hereditary thymine-uraciluria or familial pyrimidinemia. DPYD deficiency is a disease characterised by persistent urinary excretion of excessive amounts of uracil, thymine and 5-hydroxymethyluracil. Patients suffering from this disease show a severe reaction to the anticancer drug 5-fluorouracil. This reaction includes stomatitis, Leukopenia, thrombocytopenia, hair loss, diarrhea, fever, marked weight loss, cerebellar ataxia, and neurologic symptoms, progressing to semicoma.
VE:
1 * 100 µl
Artikel-Nr:
(BOSSBS-8288R-CY5.5)
Lieferant:
Bioss
Hersteller-Artikelnummer::
BS-8288R-CY5.5
Lokale Artikelnummer::
BOSSBS-8288R-CY5.5
Beschreibung:
Dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase (DPYD) catalyzes the first rate-limiting step of the NADPH-dependent catabolism of uracil and thymine to dihydrouracil and dihydrothymine; thus, a deficiency of DPYD leads to an accumulation of uracil and thymine. Abnormal concentrations of these metabolites in bodily fluids may be the cause of neurological disease and a contraindication for treatment of cancer patients with certain pyrimidine analogs. DPYD also catalyzes the anticancer agent 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) pathway and is involved in the efficacy and toxicity of 5-FU. Variations in DPYD concentration may arise from alterations at the transcriptional level of the dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase gene. Specifically, hypermethylation of the DPYD promoter downregulates dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase expression. Deficient DPYD alleles may constitute a risk factor for severe toxicity following treatment with 5-FU.Involvement in disease:Defects in DPYD are the cause of dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase deficiency (DPYD deficiency) ; also known as hereditary thymine-uraciluria or familial pyrimidinemia. DPYD deficiency is a disease characterized by persistent urinary excretion of excessive amounts of uracil, thymine and 5-hydroxymethyluracil. Patients suffering from this disease show a severe reaction to the anticancer drug 5-fluorouracil. This reaction includes stomatitis, Leukopenia, thrombocytopenia, hair loss, diarrhea, fever, marked weight loss, cerebellar ataxia, and neurologic symptoms, progressing to semicoma.
VE:
1 * 100 µl
Preis auf Anfrage
Lager für diesen Artikel ist begrenzt, kann aber in einem Lagerhaus in Ihrer Nähe zur Verfügung. Bitte stellen Sie sicher, dass Sie in sind angemeldet auf dieser Seite, so dass verfügbare Bestand angezeigt werden können. Wenn das
Lager für diesen Artikel ist begrenzt, kann aber in einem Lagerhaus in Ihrer Nähe zur Verfügung. Bitte stellen Sie sicher, dass Sie in sind angemeldet auf dieser Seite, so dass verfügbare Bestand angezeigt werden können. Wenn das
Dieses Produkt kann nur an eine Lieferadresse versandt werden die über die entsprechende Lizenzen verfügt. Für weitere Hilfe bitte kontaktieren Sie Ihr VWR Vertriebszentrum.
-Additional Documentation May be needed to purchase this item. A VWR representative will contact you if needed.
Dieses Produkt wurde von Ihrer Organisation gesperrt. Bitte kontaktieren Sie Ihren Einkauf für weitere Informationen.
Dieses Produkt ist Ersatz für den von Ihnen gewünschten Artikel.
Dieses Produkt ist nicht mehr verfügbar. Bitte kontaktieren Sie den VWR Kundenservice.
|
|||||||||