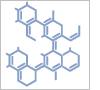
5-Carboxy-2-fluorphenylborons\u00E4ure
Artikel-Nr:
(BOSSBS-12538R-A350)
Lieferant:
Bioss
Hersteller-Artikelnummer::
BS-12538R-A350
Lokale Artikelnummer::
BOSSBS-12538R-A350
Beschreibung:
ATF2 is a member of the ATF/CREB family of basic region leucine zipper DNA binding proteins that regulates transcription by binding to a consensus cAMP response element (CRE) in the promoter of various viral and cellular genes. Many of these genes are important in cell growth and differentiation, and in stress and immune responses. ATF2 is a nuclear protein that binds DNA as a dimer and can form dimers with members of the ATF/CREB and Jun/Fos families. It is a stronger activator as a heterodimer with cJun than as a homodimer. Several isoforms of ATF2 arise by differential splicing. The stable native full length ATF2 is transcriptionally inactive as a result of an inhibitory direct intramolecular interaction of its carboxy terminal DNA binding domain with the amino terminal transactivation domain. Following dimerization ATF2 becomes a short lived protein that undergoes ubiquitination and proteolysis, seemingly in a protein phosphatase-dependent mechanism. Stimulation of the transcriptional activity of ATF2 occurs following cellular stress induced by several genotoxic agents, inflammatory cytokines, and UV irradiation. This activation requires phosphorylation of two threonine residues in ATF2 by both JNK/SAP kinase and p38 MAP kinase. ATF2 is abundantly expressed in brain.
VE:
1 * 100 µl
Artikel-Nr:
(BOSSBS-12538R-A555)
Lieferant:
Bioss
Hersteller-Artikelnummer::
BS-12538R-A555
Lokale Artikelnummer::
BOSSBS-12538R-A555
Beschreibung:
ATF2 is a member of the ATF/CREB family of basic region leucine zipper DNA binding proteins that regulates transcription by binding to a consensus cAMP response element (CRE) in the promoter of various viral and cellular genes. Many of these genes are important in cell growth and differentiation, and in stress and immune responses. ATF2 is a nuclear protein that binds DNA as a dimer and can form dimers with members of the ATF/CREB and Jun/Fos families. It is a stronger activator as a heterodimer with cJun than as a homodimer. Several isoforms of ATF2 arise by differential splicing. The stable native full length ATF2 is transcriptionally inactive as a result of an inhibitory direct intramolecular interaction of its carboxy terminal DNA binding domain with the amino terminal transactivation domain. Following dimerization ATF2 becomes a short lived protein that undergoes ubiquitination and proteolysis, seemingly in a protein phosphatase-dependent mechanism. Stimulation of the transcriptional activity of ATF2 occurs following cellular stress induced by several genotoxic agents, inflammatory cytokines, and UV irradiation. This activation requires phosphorylation of two threonine residues in ATF2 by both JNK/SAP kinase and p38 MAP kinase. ATF2 is abundantly expressed in brain.
VE:
1 * 100 µl
Artikel-Nr:
(BOSSBS-12539R-A350)
Lieferant:
Bioss
Hersteller-Artikelnummer::
BS-12539R-A350
Lokale Artikelnummer::
BOSSBS-12539R-A350
Beschreibung:
ATF2 is a member of the ATF/CREB family of basic region leucine zipper DNA binding proteins that regulates transcription by binding to a consensus cAMP response element (CRE) in the promoter of various viral and cellular genes. Many of these genes are important in cell growth and differentiation, and in stress and immune responses. ATF2 is a nuclear protein that binds DNA as a dimer and can form dimers with members of the ATF/CREB and Jun/Fos families. It is a stronger activator as a heterodimer with cJun than as a homodimer. Several isoforms of ATF2 arise by differential splicing. The stable native full length ATF2 is transcriptionally inactive as a result of an inhibitory direct intramolecular interaction of its carboxy terminal DNA binding domain with the amino terminal transactivation domain. Following dimerization ATF2 becomes a short lived protein that undergoes ubiquitination and proteolysis, seemingly in a protein phosphatase-dependent mechanism. Stimulation of the transcriptional activity of ATF2 occurs following cellular stress induced by several genotoxic agents, inflammatory cytokines, and UV irradiation. This activation requires phosphorylation of two threonine residues in ATF2 by both JNK/SAP kinase and p38 MAP kinase. ATF2 is abundantly expressed in brain.
VE:
1 * 100 µl
Artikel-Nr:
(BOSSBS-5170R-FITC)
Lieferant:
Bioss
Hersteller-Artikelnummer::
BS-5170R-FITC
Lokale Artikelnummer::
BOSSBS-5170R-FITC
Beschreibung:
ATF2 is a member of the ATF/CREB family of basic region leucine zipper DNA binding proteins that regulates transcription by binding to a consensus cAMP response element (CRE) in the promoter of various viral and cellular genes. Many of these genes are important in cell growth and differentiation, and in stress and immune responses. ATF2 is a nuclear protein that binds DNA as a dimer and can form dimers with members of the ATF/CREB and Jun/Fos families. It is a stronger activator as a heterodimer with cJun than as a homodimer. Several isoforms of ATF2 arise by differential splicing. The stable native full length ATF2 is transcriptionally inactive as a result of an inhibitory direct intramolecular interaction of its carboxy terminal DNA binding domain with the amino terminal transactivation domain. Following dimerization ATF2 becomes a short lived protein that undergoes ubiquitination and proteolysis, seemingly in a protein phosphatase-dependent mechanism. Stimulation of the transcriptional activity of ATF2 occurs following cellular stress induced by several genotoxic agents, inflammatory cytokines, and UV irradiation. This activation requires phosphorylation of two threonine residues in ATF2 by both JNK/SAP kinase and p38 MAP kinase. ATF2 is abundantly expressed in brain.
VE:
1 * 100 µl
Artikel-Nr:
(PRSI7183P)
Lieferant:
ProSci Inc.
Hersteller-Artikelnummer::
7183P
Lokale Artikelnummer::
PRSI7183P
Beschreibung:
17 amino acids near the carboxy terminus of human BCL3.
VE:
1 * 50 µG
Artikel-Nr:
(PRSI7191P)
Lieferant:
ProSci Inc.
Hersteller-Artikelnummer::
7191P
Lokale Artikelnummer::
PRSI7191P
Beschreibung:
13 amino acids near the carboxy terminus of human PTGDR2.
VE:
1 * 50 µG
Artikel-Nr:
(PRSI7389P)
Lieferant:
ProSci Inc.
Hersteller-Artikelnummer::
7389P
Lokale Artikelnummer::
PRSI7389P
Beschreibung:
19 amino acids near the carboxy terminus of human DAP.
VE:
1 * 50 µG
Artikel-Nr:
(PRSI7291P)
Lieferant:
ProSci Inc.
Hersteller-Artikelnummer::
7291P
Lokale Artikelnummer::
PRSI7291P
Beschreibung:
15 amino acids near the carboxy terminus of human TMEM135.
VE:
1 * 50 µG
Artikel-Nr:
(PRSI7201P)
Lieferant:
ProSci Inc.
Hersteller-Artikelnummer::
7201P
Lokale Artikelnummer::
PRSI7201P
Beschreibung:
17 amino acids near the carboxy terminus of human CCL2.
VE:
1 * 50 µG
Artikel-Nr:
(PRSI7163P)
Lieferant:
ProSci Inc.
Hersteller-Artikelnummer::
7163P
Lokale Artikelnummer::
PRSI7163P
Beschreibung:
19 amino acids near the carboxy terminus of human DHX36.
VE:
1 * 50 µG
Artikel-Nr:
(PRSI7283P)
Lieferant:
ProSci Inc.
Hersteller-Artikelnummer::
7283P
Lokale Artikelnummer::
PRSI7283P
Beschreibung:
17 amino acids near the carboxy terminus of human MTERFD2.
VE:
1 * 50 µG
Artikel-Nr:
(PRSI7195P)
Lieferant:
ProSci Inc.
Hersteller-Artikelnummer::
7195P
Lokale Artikelnummer::
PRSI7195P
Beschreibung:
15 amino acids near the carboxy terminus of human STAT1.
VE:
1 * 50 µG
Artikel-Nr:
(BOSSBS-7594R-A488)
Lieferant:
Bioss
Hersteller-Artikelnummer::
BS-7594R-A488
Lokale Artikelnummer::
BOSSBS-7594R-A488
Beschreibung:
Ankyrins are a family of proteins that link the integral membrane proteins to the underlying spectrin-actin cytoskeleton and play key roles in activities such as cell motility, activation, proliferation, contact and the maintenance of specialized membrane domains. Multiple isoforms of ankyrin with different affinities for various target proteins are expressed in a tissue-specific, developmentally regulated manner. Most ankyrins are typically composed of three structural domains: an amino-terminal domain containing multiple ankyrin repeats; a central region with a highly conserved spectrin binding domain; and a carboxy-terminal regulatory domain which is the least conserved and subject to variation. Ankyrin 1, the prototype of this family, was first discovered in the erythrocytes, but since has also been found in brain and muscles. Mutations in erythrocytic ankyrin 1 have been associated in approximately half of all patients with hereditary spherocytosis. Complex patterns of alternative splicing in the regulatory domain, giving rise to different isoforms of ankyrin 1 have been described. Truncated muscle-specific isoforms of ankyrin1 resulting from usage of an alternate promoter have also been identified. [provided by RefSeq, Dec 2008].
VE:
1 * 100 µl
Artikel-Nr:
(BOSSBS-7594R-A350)
Lieferant:
Bioss
Hersteller-Artikelnummer::
BS-7594R-A350
Lokale Artikelnummer::
BOSSBS-7594R-A350
Beschreibung:
Ankyrins are a family of proteins that link the integral membrane proteins to the underlying spectrin-actin cytoskeleton and play key roles in activities such as cell motility, activation, proliferation, contact and the maintenance of specialized membrane domains. Multiple isoforms of ankyrin with different affinities for various target proteins are expressed in a tissue-specific, developmentally regulated manner. Most ankyrins are typically composed of three structural domains: an amino-terminal domain containing multiple ankyrin repeats; a central region with a highly conserved spectrin binding domain; and a carboxy-terminal regulatory domain which is the least conserved and subject to variation. Ankyrin 1, the prototype of this family, was first discovered in the erythrocytes, but since has also been found in brain and muscles. Mutations in erythrocytic ankyrin 1 have been associated in approximately half of all patients with hereditary spherocytosis. Complex patterns of alternative splicing in the regulatory domain, giving rise to different isoforms of ankyrin 1 have been described. Truncated muscle-specific isoforms of ankyrin1 resulting from usage of an alternate promoter have also been identified. [provided by RefSeq, Dec 2008].
VE:
1 * 100 µl
Artikel-Nr:
(BOSSBS-12536R-CY5)
Lieferant:
Bioss
Hersteller-Artikelnummer::
BS-12536R-CY5
Lokale Artikelnummer::
BOSSBS-12536R-CY5
Beschreibung:
ATF2 is a member of the ATF/CREB family of basic region leucine zipper DNA binding proteins that regulates transcription by binding to a consensus cAMP response element (CRE) in the promoter of various viral and cellular genes. Many of these genes are important in cell growth and differentiation, and in stress and immune responses. ATF2 is a nuclear protein that binds DNA as a dimer and can form dimers with members of the ATF/CREB and Jun/Fos families. It is a stronger activator as a heterodimer with cJun than as a homodimer. Several isoforms of ATF2 arise by differential splicing. The stable native full length ATF2 is transcriptionally inactive as a result of an inhibitory direct intramolecular interaction of its carboxy terminal DNA binding domain with the amino terminal transactivation domain. Following dimerization ATF2 becomes a short lived protein that undergoes ubiquitination and proteolysis, seemingly in a protein phosphatase-dependent mechanism. Stimulation of the transcriptional activity of ATF2 occurs following cellular stress induced by several genotoxic agents, inflammatory cytokines, and UV irradiation. This activation requires phosphorylation of two threonine residues in ATF2 by both JNK/SAP kinase and p38 MAP kinase. ATF2 is abundantly expressed in brain.
VE:
1 * 100 µl
Artikel-Nr:
(BOSSBS-12538R-CY3)
Lieferant:
Bioss
Hersteller-Artikelnummer::
BS-12538R-CY3
Lokale Artikelnummer::
BOSSBS-12538R-CY3
Beschreibung:
ATF2 is a member of the ATF/CREB family of basic region leucine zipper DNA binding proteins that regulates transcription by binding to a consensus cAMP response element (CRE) in the promoter of various viral and cellular genes. Many of these genes are important in cell growth and differentiation, and in stress and immune responses. ATF2 is a nuclear protein that binds DNA as a dimer and can form dimers with members of the ATF/CREB and Jun/Fos families. It is a stronger activator as a heterodimer with cJun than as a homodimer. Several isoforms of ATF2 arise by differential splicing. The stable native full length ATF2 is transcriptionally inactive as a result of an inhibitory direct intramolecular interaction of its carboxy terminal DNA binding domain with the amino terminal transactivation domain. Following dimerization ATF2 becomes a short lived protein that undergoes ubiquitination and proteolysis, seemingly in a protein phosphatase-dependent mechanism. Stimulation of the transcriptional activity of ATF2 occurs following cellular stress induced by several genotoxic agents, inflammatory cytokines, and UV irradiation. This activation requires phosphorylation of two threonine residues in ATF2 by both JNK/SAP kinase and p38 MAP kinase. ATF2 is abundantly expressed in brain.
VE:
1 * 100 µl
Preis auf Anfrage
Lager für diesen Artikel ist begrenzt, kann aber in einem Lagerhaus in Ihrer Nähe zur Verfügung. Bitte stellen Sie sicher, dass Sie in sind angemeldet auf dieser Seite, so dass verfügbare Bestand angezeigt werden können. Wenn das
Lager für diesen Artikel ist begrenzt, kann aber in einem Lagerhaus in Ihrer Nähe zur Verfügung. Bitte stellen Sie sicher, dass Sie in sind angemeldet auf dieser Seite, so dass verfügbare Bestand angezeigt werden können. Wenn das
Dieses Produkt kann nur an eine Lieferadresse versandt werden die über die entsprechende Lizenzen verfügt. Für weitere Hilfe bitte kontaktieren Sie Ihr VWR Vertriebszentrum.
-Additional Documentation May be needed to purchase this item. A VWR representative will contact you if needed.
Dieses Produkt wurde von Ihrer Organisation gesperrt. Bitte kontaktieren Sie Ihren Einkauf für weitere Informationen.
Dieses Produkt ist Ersatz für den von Ihnen gewünschten Artikel.
Dieses Produkt ist nicht mehr verfügbar. Bitte kontaktieren Sie den VWR Kundenservice.
|
|||||||||